The Goods and Services Tax (GST) system in India has brought transparency and efficiency to the country’s taxation framework.
However, compliance can sometimes feel overwhelming due to the various forms and reports involved. Among these, GSTR-2A and GSTR-2B are vital for reconciling Input Tax Credit (ITC).
If you’ve ever wondered why there are two similar-sounding reports and how they differ, this blog will help you untangle the confusion.
What is GSTR-2A?
GSTR-2A is an auto-generated report in the GST portal that reflects details of all invoices uploaded by your suppliers.
Think of it as a dynamic ledger that gets updated every time a supplier submits or modifies their GSTR-1, GSTR-5, or other relevant returns.
Here’s why GSTR-2A is important:
- Real-time updates: It allows businesses to track invoices and GST payments as suppliers upload data.
- Dynamic nature: Changes made by suppliers—such as invoice amendments—are immediately reflected.
For example, if your supplier uploads a missing invoice today, it will instantly appear in your GSTR-2A.
What is GSTR-2B?
GSTR-2B, on the other hand, is a static report generated monthly. Unlike GSTR-2A, it provides a snapshot of eligible ITC for a specific tax period.
The report includes details of invoices, credit notes, and other relevant documents submitted by suppliers.
Key highlights of GSTR-2B:
- Fixed period: It doesn’t change once generated, making it ideal for ITC claims.
- Consolidated data: It compiles data across all supplier filings for a given month.
This static nature ensures consistency and prevents last-minute changes while claiming ITC.
What Are the Benefits of GSTR-2A and GSTR-2B
Benefits of GSTR-2A
- Real-time tracking: GSTR-2A provides live updates, helping businesses keep track of invoices uploaded by suppliers.
- Improved transparency: It ensures that businesses can see what their suppliers have filed, promoting better vendor compliance.
- Early error detection: With dynamic updates, businesses can quickly identify mismatches or missing invoices and address them proactively.
- Simplified reconciliation: Continuous updates make it easier to match invoices with purchase registers before the tax period ends.
Benefits of GSTR-2B
- Static and reliable: GSTR-2B provides a stable snapshot of ITC eligibility, reducing last-minute changes or confusion.
- Supports accurate ITC claims: Its consolidated nature ensures businesses claim only the eligible ITC for a specific tax period, minimizing errors.
- Time-saving: By offering a finalized view of ITC, it streamlines the filing process and eliminates the need for extensive reconciliation during return submission.
- Compliance assurance: With GSTR-2B, businesses can be confident in meeting GST compliance requirements by relying on accurate and unchanging data.
Key Differences Between GSTR-2A and GSTR-2B
Here’s a quick look at how GSTR-2A and GSTR-2B differ:
| Feature | GSTR-2A | GSTR-2B |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Dynamic | Static |
| Updates | Real-time | Fixed monthly snapshot |
| Purpose | Reconciliation of invoices | ITC eligibility for a period |
| Source | Data from supplier filings | Consolidated supplier data |
| Period Coverage | Continuously updates over time | Specific tax period |
While GSTR-2A is a live tracker, GSTR-2B is like a final ITC statement for the month.
When to Use GSTR-2A and GSTR-2B?
The choice between GSTR-2A and GSTR-2B depends on your purpose:
Use GSTR-2A when:
- You’re reconciling invoices throughout the month.
- Resolving mismatches with suppliers.
- Tracking real-time compliance by vendors.
Use GSTR-2B when:
- Filing your monthly GST returns.
- Calculating final ITC for the tax period.
- Avoiding discrepancies in ITC claims.
For example, while GSTR-2A helps identify missing invoices during the month, GSTR-2B ensures that only eligible ITC for the period is claimed.
How to Reconcile Using GSTR-2A and GSTR-2B
Reconciling ITC can be straightforward if you use both reports effectively. Here’s a step-by-step approach:
- Download GSTR-2A and GSTR-2B: Start by accessing these reports from the GST portal.
- Match invoices: Compare the invoices in both reports with your purchase register.
- Identify mismatches: Check for any discrepancies—such as missing or amended invoices—that appear in GSTR-2A but not in GSTR-2B.
- Communicate with suppliers: Resolve any mismatches by asking suppliers to update their filings.
- Claim ITC based on GSTR-2B: Use the static GSTR-2B report for your final ITC claim to ensure compliance.
Technology tools can simplify this process by automating reconciliation and highlighting discrepancies.
Suvit offers this facility, take a quick look at it:
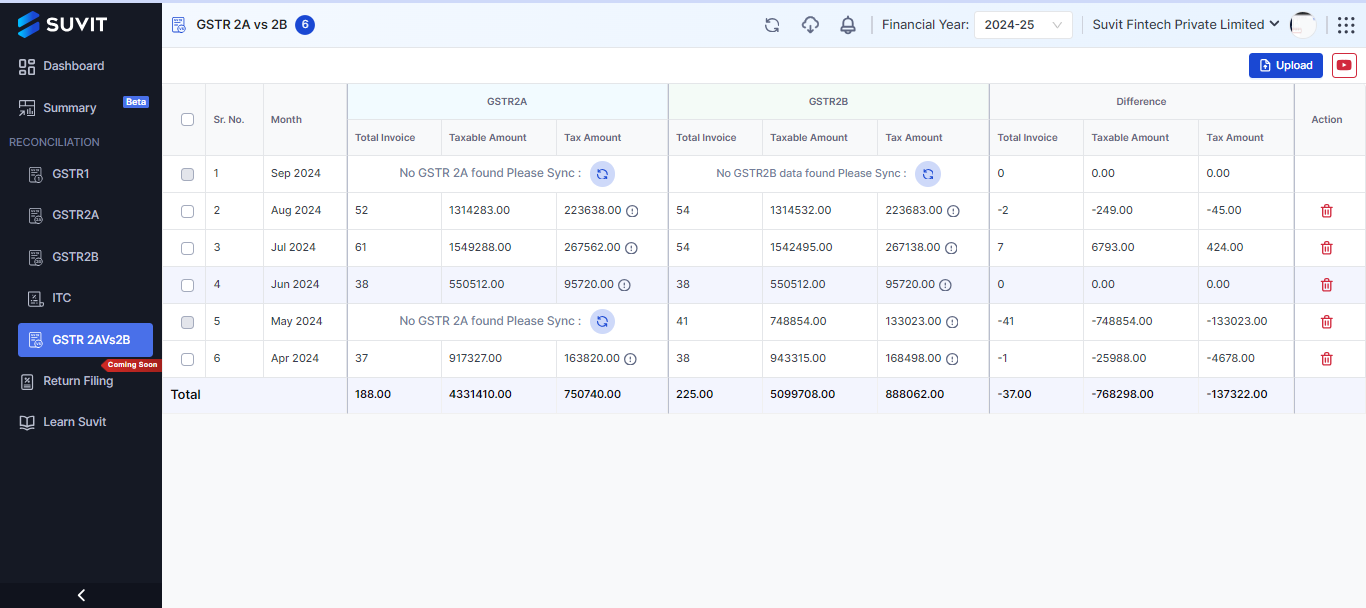
To know more about Suvit’s GST Reco feature, take a look here!
You can try Suvit for free for a week to know this whole process.
Technology For Rescue
Understanding the difference between GSTR-2A and GSTR-2B can significantly simplify your GST compliance process.
While GSTR-2A offers real-time tracking for reconciliation, GSTR-2B provides a stable, finalized view of ITC eligibility for a specific period. Using both effectively ensures accurate filings and avoids penalties.
Leverage technology to automate reconciliation, reduce manual errors, and stay ahead in your GST compliance journey. By mastering these reports, you’ll not only save time but also maximize your eligible tax credit seamlessly.
Also Read: 7 Easy Steps for Flawless GSTR 2A Reconciliation in Tally
FAQs
What happens if there’s a mismatch between GSTR-2A and GSTR-2B?
Mismatches often arise due to delayed or incomplete filing by suppliers. In such cases, contact the supplier to correct their filings. Remember, ITC claims are restricted to the data in GSTR-2B.
Can both reports be used together for reconciliation?
Indeed, businesses should use GSTR-2B for final ITC claims and GSTR-2A for continuing reconciliation. This dual approach minimizes errors.
Why are ITC claims restricted to GSTR-2B?
GSTR-2B provides a static and consistent snapshot, ensuring businesses claim ITC only for invoices submitted within the applicable period, thus avoiding compliance issues.












